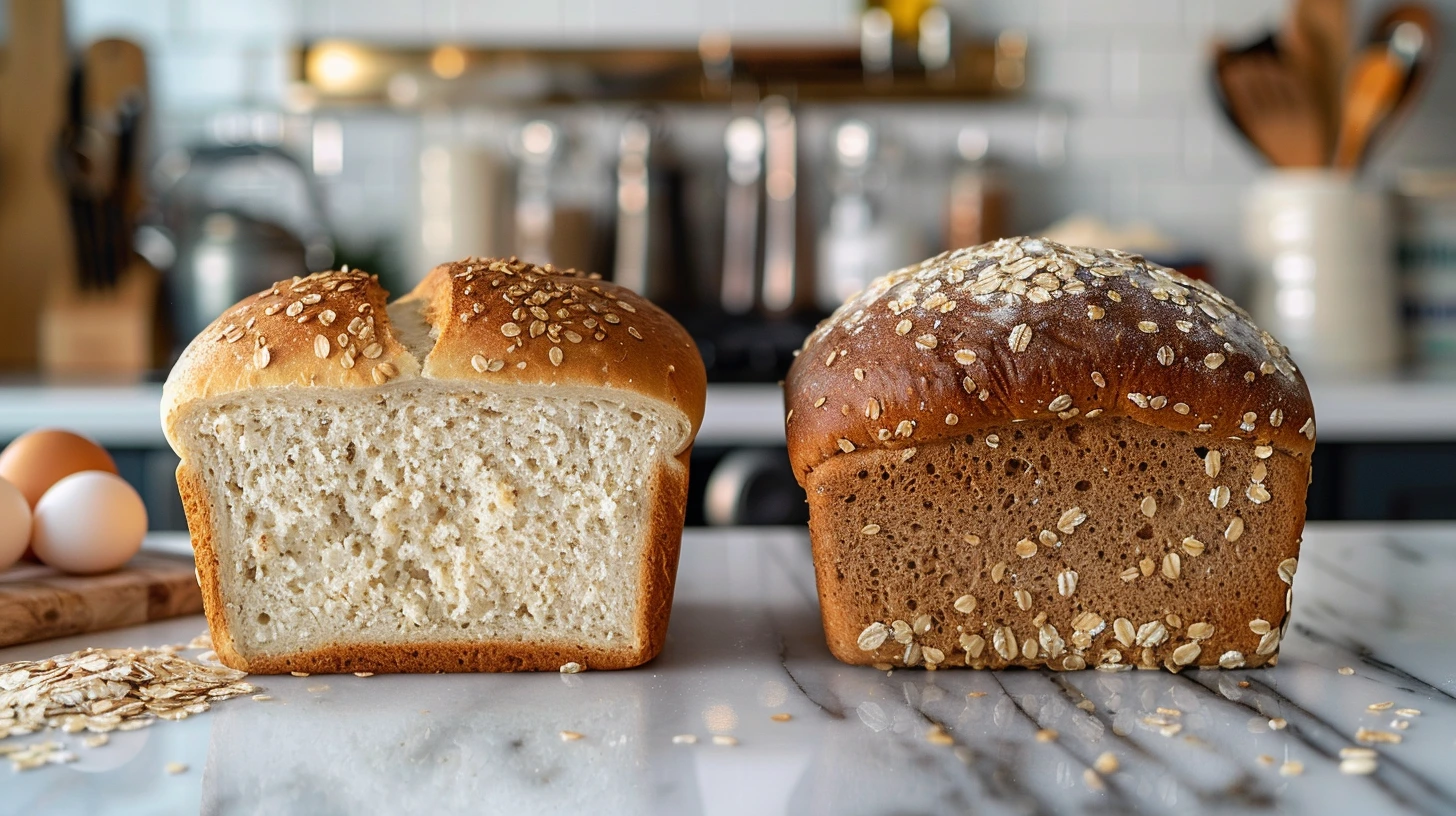
Bread is a staple for many, but choosing between oat bread and white bread can be confusing. Each has its pros and cons, but understanding their differences is key to picking the right one for your diet. Oat bread is known for its higher fiber and nutrient content, while white bread is often fortified with essential vitamins. Let’s explore which bread suits your needs better.
For those who enjoy baking, check out this step-by-step oat molasses bread recipe to make a nutritious loaf at home.
What is Oat Bread?

Oat bread is a hearty bread made primarily from oat flour or whole oats. It is popular for its dense texture and natural ingredients.
Ingredients in Oat Bread
- Oats: A rich source of soluble fiber.
- Whole-Grain Flours: Commonly mixed for additional texture.
- Seeds or Nuts: Sometimes added for flavor and nutrients.
Why Choose Oat Bread?
Oat bread offers:
- High Fiber Content: Essential for digestion and satiety.
- Beta-Glucan: A special fiber linked to cholesterol reduction.
- Nutrient Density: Packed with magnesium, manganese, and selenium.
What is White Bread?

White bread is made from refined wheat flour, offering a softer texture and lighter flavor. It’s a popular choice for sandwiches and toast.
Ingredients in White Bread
- Refined Wheat Flour: Stripped of the bran and germ during processing.
- Fortified Nutrients: Often enriched with folic acid, calcium, and iron.
Why Choose White Bread?
Despite its reputation, white bread has some advantages:
- Fortification: Adds essential nutrients like iron and folate.
- Soft Texture: Ideal for people with sensitive digestion.
- Quick Energy: High in simple carbohydrates for fast fuel.
Looking for a twist on white bread? Explore this gut-healing bread recipe without eggs for more creative options.
Nutritional Comparison: Oat Bread vs. White Bread
Understanding the differences in their nutritional profiles can help you decide.
Macronutrients
- Calories: White bread contains slightly more calories per slice.
- Fiber: Oat bread surpasses white bread, aiding digestion and improving satiety.
- Protein: Both are similar, though oat bread may contain more protein due to added seeds or grains.
Micronutrients
- Oat Bread: High in selenium, manganese, and magnesium.
- White Bread: Fortified with folic acid, iron, and calcium.
Discover the full nutritional breakdown of white bread here to see how it compares to other bread types.
Health Benefits of Oat Bread
Oat bread is a favorite among health-conscious individuals due to its numerous benefits.
1. Rich in Fiber
Its high fiber content:
- Improves digestion.
- Keeps you full for longer.
- Helps regulate blood sugar levels.
2. Supports Heart Health
Oat bread contains beta-glucan, a type of soluble fiber that:
- Reduces cholesterol.
- Enhances cardiovascular health.
Health Benefits of White Bread
While often criticized, white bread does have its own set of benefits.
1. Fortified Nutrients
White bread often includes added vitamins such as:
- Iron: Supports healthy blood cells.
- Folic Acid: Essential for pregnant women and neural health.
2. Accessibility
White bread is affordable and widely available, making it a convenient choice for many households.
Environmental Impact of Oat Bread and White Bread
Another angle to consider is the environmental impact of these bread types.
Sustainability of Oats
Oats are considered more sustainable than wheat due to:
- Lower water usage during cultivation.
- Better adaptability to different climates.
- Contribution to soil health through crop rotation.
Environmental Costs of White Bread
White bread production, relying on refined wheat, involves:
- High energy consumption for processing.
- Greater resource depletion due to monoculture farming.
How to Incorporate More Oat Bread in Your Diet
If you’re looking to include more oat bread in your meals, here are some tips.
Breakfast Ideas
- Toast oat bread with avocado or almond butter.
- Pair it with eggs for a protein-rich start to your day.
Lunch Options
- Make a hearty sandwich with lean protein and fresh veggies.
- Use it as a base for an open-faced salmon or chicken salad sandwich.
For more bread recipe inspiration, try this easy sourdough recipe without a starter.
When to Choose Each Bread
The decision depends on your lifestyle and dietary needs.
Opt for Oat Bread if:
- You prioritize fiber and long-lasting energy.
- You’re managing diabetes or heart health.
Opt for White Bread if:
- You need a quick, affordable option.
- You require fortified nutrients for specific dietary needs.
FAQs: Is Oat Bread Better Than White Bread?
1. Is oat bread better for digestion?
Yes, the high fiber content in oat bread supports better digestion compared to white bread.
2. Which bread is better for weight loss?
Oat bread is more filling and can help reduce overall calorie intake.
3. Can white bread still be healthy?
Yes, when eaten in moderation and combined with nutrient-dense foods, white bread can be part of a balanced diet.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Bread for You
When deciding between oat bread and white bread, consider your health goals. If fiber and nutrients are your priority, oat bread is the better option. However, white bread can still serve as a convenient and fortified choice.
For a creative twist on baking, explore recipes like this oat molasses bread guide or this gut-healing bread recipe. Whatever you choose, balance your diet for the best results!