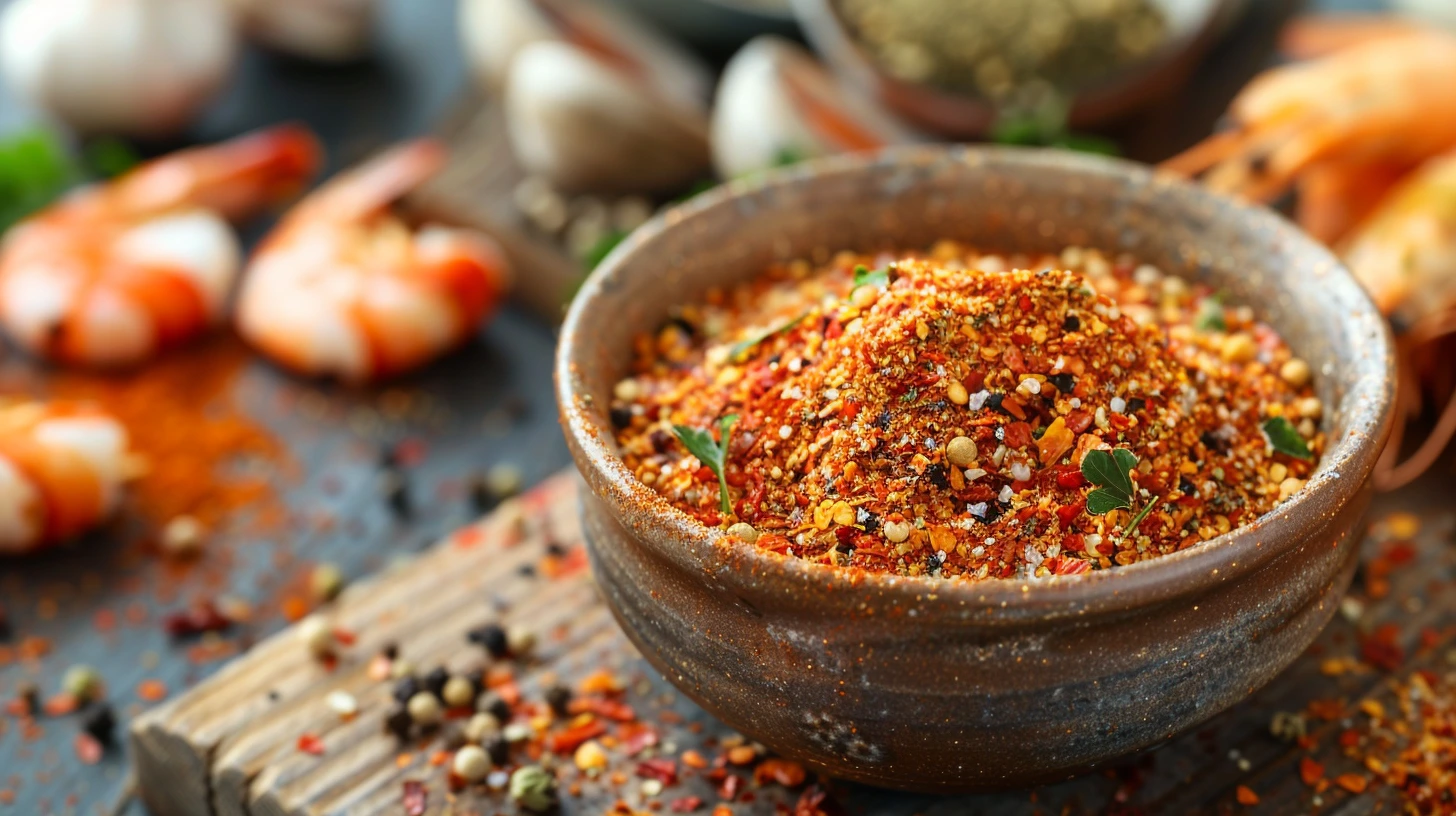
Introduction to Seafood Seasoning
Seafood seasoning is the ultimate companion for enhancing the natural flavors of ocean delicacies. From its tantalizing aroma to its ability to elevate even the simplest seafood dishes, the right seasoning blend can make all the difference. Whether you’re grilling shrimp, steaming mussels, or roasting fish, a perfectly balanced mix of spices and herbs will bring out the best in your meal.
This article delves deep into the world of seafood seasoning, exploring its history, ingredients, and culinary uses. Whether you’re a home cook or a seasoned chef, you’ll find tips and recipes to take your seafood creations to the next level.
The History and Origins of Seafood Seasoning
Seafood seasoning, as we know it today, is a product of centuries of culinary evolution and cultural exchanges. Its creation stems from the desire to enhance the flavors of fish and shellfish while complementing their delicate natural taste.
If you’re exploring seasonings for different cuisines, check out this Hillbilly Fish Seasoning Recipe for a Southern twist.
Regional Influences on Flavor Profiles
Different regions have influenced the development of seafood seasoning, giving rise to unique flavor profiles:
- Mediterranean Coastal Regions
- In Mediterranean cuisine, seafood seasoning often includes aromatic herbs like oregano, thyme, and parsley, along with citrus zest and olive oil. These flavors highlight the freshness of the seafood while adding a subtle earthiness.
- Asian Coastal Traditions
- Asian seafood seasonings incorporate bold spices like ginger, garlic, and chili, along with soy sauce and sesame oil. For instance, in Japanese cuisine, seaweed and miso are common additives for umami richness.
- American Coastal Favorites
- The Southern United States, particularly the Gulf Coast, is known for Cajun and Creole seafood blends. These spicy and smoky seasonings include paprika, cayenne pepper, and garlic powder.
- Caribbean Influences
- Caribbean seafood blends often feature tropical spices like allspice, nutmeg, and cloves, paired with citrus and herbs for a vibrant, aromatic finish.
Traditional Uses in Coastal Cuisines
Seafood seasoning has been an integral part of coastal cuisines worldwide. Traditionally, it was used for:
- Preservation: Salt, a key ingredient in many blends, was used to preserve fish before refrigeration.
- Flavor Enhancement: Spices like black pepper, paprika, and cumin were added to mask the fishy odor while intensifying the taste.
- Cultural Identity: Each region’s choice of spices and herbs reflects its cultural history, trading influences, and local ingredients.
Essential Ingredients in Seafood Seasoning
Crafting the perfect seafood seasoning requires a careful balance of spices, herbs, and other flavor-enhancing ingredients. These components work together to elevate seafood dishes while complementing their natural flavors.
The Core Spices
- Salt
- Salt forms the foundation of most seafood seasoning blends. It enhances the seafood’s natural taste and acts as a flavor amplifier for other ingredients.
- Black Pepper
- This classic spice adds a mild heat and subtle earthiness, balancing the blend’s overall flavor.
- Paprika
- Paprika contributes a vibrant color and a smoky or sweet flavor, depending on the variety used.
- Cayenne Pepper
- For those who enjoy a spicy kick, cayenne pepper adds heat and depth to the seasoning.
- Garlic Powder
- Garlic powder provides a savory, umami flavor that complements the delicate taste of seafood.
- Onion Powder
- Onion powder adds a touch of sweetness and a rounded flavor to the blend.
Additives for Complexity
- Lemon Zest or Citric Acid
- These ingredients introduce a tangy, citrusy brightness that pairs beautifully with fish and shellfish.
- Sugar or Brown Sugar
- A small amount of sugar can balance the saltiness and spices, especially in smoky or spicy blends.
- Smoked Salt or Liquid Smoke
- These additives impart a smoky aroma, ideal for grilled or roasted seafood.
Common Herbs in Seafood Blends
- Dill
- A traditional herb for seafood, dill has a grassy, slightly tangy flavor that enhances fish and shellfish.
- Parsley
- Fresh or dried parsley adds a mild, peppery flavor and a touch of greenery.
- Thyme
- This aromatic herb contributes earthy and floral notes, ideal for baked or broiled seafood.
- Bay Leaves
- Often included in broths or stews, bay leaves add a subtle depth of flavor to seafood dishes.
- Oregano or Marjoram
- These herbs lend a Mediterranean flair to seafood seasoning blends.
How to Make Homemade Seafood Seasoning
Making your own seafood seasoning at home is a rewarding way to customize flavors to your liking. With a few common spices and herbs, you can create a blend that enhances your seafood dishes while catering to your unique taste preferences.
Tools and Ingredients Needed
Tools:
- Mixing bowl
- Measuring spoons
- Airtight container or spice jar for storage
- Mortar and pestle or spice grinder (optional, for fresh grinding)
Base Ingredients:
- 2 tablespoons of salt
- 1 tablespoon of black pepper
- 1 tablespoon of paprika (sweet or smoked)
- 1 teaspoon of cayenne pepper (adjust based on desired spiciness)
- 1 tablespoon of garlic powder
- 1 tablespoon of onion powder
Optional Additions for Customization:
- 1 teaspoon of dried dill or parsley
- 1 teaspoon of thyme or oregano
- 1 teaspoon of lemon zest or citric acid
- 1 teaspoon of sugar or brown sugar for sweetness
Step-by-Step Guide to Crafting the Perfect Blend
- Gather and Measure Ingredients
- Lay out all the spices and herbs, measuring each one accurately to ensure balance in your blend.
- Combine the Spices
- In a mixing bowl, combine salt, black pepper, paprika, cayenne pepper, garlic powder, and onion powder. Stir well until evenly mixed.
- Incorporate Optional Ingredients
- If using additional herbs like dill or parsley, add them to the mixture. For a tangy kick, mix in lemon zest or citric acid. Adjust sweetness by adding sugar if desired.
- Grind or Crush (Optional)
- For a smoother texture, use a mortar and pestle or spice grinder to blend the seasonings further. This step is especially helpful if you’ve included coarse salt or dried herbs.
- Store Properly
- Transfer the seasoning to an airtight container or spice jar. Label the jar with the date and contents to ensure freshness.
- Taste and Adjust
- Before using the blend, test it on a small piece of seafood or sprinkle it on vegetables. Adjust the salt, spice, or herbs as needed to match your preferences.
Tips for Customizing Flavors
- For Spicy Lovers: Add more cayenne pepper or crushed red pepper flakes.
- For a Smoky Touch: Use smoked paprika or smoked salt.
- For Citrus Fans: Incorporate extra lemon zest or dried lime powder.
- For Subtle Sweetness: Add a pinch of cinnamon or nutmeg for a unique depth of flavor.
For an elevated seafood experience, try pairing your seasoning with this Grilled Dorado Fish Recipe.
Popular Store-Bought Seafood Seasonings
If you prefer the convenience of pre-made blends, store-bought seafood seasonings offer a variety of options to suit different tastes and cooking styles. Understanding their unique flavors and ingredients can help you choose the right product for your kitchen.
Iconic Brands and Their Signature Blends
- Old Bay Seasoning
- Flavor Profile: A classic blend of celery salt, paprika, black pepper, and other spices.
- Best For: Crab, shrimp boils, and grilled fish.
- Why It’s Popular: Old Bay has become synonymous with seafood seasoning in the United States, particularly in Maryland-style crab dishes.
- Zatarain’s Crab Boil
- Flavor Profile: A bold, spicy mix of mustard seeds, coriander, cayenne, and bay leaves.
- Best For: Boiling shellfish like shrimp, crabs, and crawfish.
- Why It’s Popular: Known for its robust and spicy kick, perfect for Southern-style seafood feasts.
- Tony Chachere’s Creole Seasoning
- Flavor Profile: A spicy Creole blend featuring garlic, cayenne, and other robust spices.
- Best For: Blackened fish, gumbo, and seafood pasta.
- Why It’s Popular: Tony Chachere’s is a household name in Creole and Cajun cooking, celebrated for its versatility.
- McCormick Grill Mates Seafood Seasoning
- Flavor Profile: A blend of lemon, garlic, and herbs with a hint of black pepper.
- Best For: Grilled salmon, shrimp, or mahi-mahi.
- Why It’s Popular: Ideal for grilling, with a focus on enhancing seafood’s natural flavors without overpowering them.
- Chef Paul Prudhomme’s Seafood Magic
- Flavor Profile: A balanced mix of paprika, thyme, and white pepper.
- Best For: Pan-seared fish, seafood soups, and stews.
- Why It’s Popular: This blend is favored for its versatility and ability to elevate delicate seafood flavors.
How to Choose the Right Product
- Consider Your Cooking Style
- For grilling: Look for blends with smoky or herbal notes.
- For boiling: Opt for bold, spicy blends like Zatarain’s or Old Bay.
- For delicate dishes: Choose lighter blends with lemon and herbs.
- Check the Ingredients
- Avoid blends with excessive salt if you’re monitoring sodium intake.
- Look for natural, preservative-free options for a healthier choice.
- Think About Pairing
- Pair spicy blends with robust seafood like shrimp or lobster.
- Use herbaceous blends for mild fish like cod or tilapia.
- Experiment with Small Quantities
- Start with smaller containers to test a brand’s flavor before committing to larger purchases.
Homemade vs. Store-Bought: Which is Better?
- Homemade Seasoning allows for full customization and control over the ingredients.
- Store-Bought Blends offer convenience and consistent flavor profiles, ideal for quick meals.
Seafood seasoning is an indispensable ingredient that enhances the natural flavors of seafood. Because of its versatility, it has become a staple in kitchens worldwide, whether you’re preparing a quick weekday meal or an elaborate seafood spread. Below are several ways you can use seafood seasoning to transform your dishes.
As a Dry Rub for Grilled and Roasted Seafood
Using seafood seasoning as a dry rub is one of the most effective methods to impart bold flavors to seafood. For example, coating fish like salmon, trout, or tuna with the seasoning before grilling creates a delicious crust. Furthermore, you can toss shrimp or scallops in olive oil and the seasoning mix, then roast them for a quick and flavorful meal. In addition, rubbing the seasoning onto shellfish, such as lobster tails or crab legs, enhances their natural sweetness during baking or steaming. Consequently, applying the seasoning before cooking allows the flavors to penetrate the seafood, resulting in a perfectly seasoned dish.
Enhancing Soups, Stews, and Broths
Seafood seasoning is also an excellent way to add depth and complexity to liquid-based dishes. For instance, sprinkling it into clam chowder or seafood bisque enriches the savory profile. Additionally, it works well in stews like gumbo or bouillabaisse, where it enhances the richness of the dish’s base. Moreover, adding it to fish broth infuses the stock with aromatic spices, making it a flavorful foundation for other recipes. Therefore, seafood seasoning serves as a key component in achieving hearty and satisfying soups and stews.
Pairing Seasoning with Different Types of Seafood
Seafood seasoning pairs differently with various types of seafood, ensuring that each dish reaches its full flavor potential.
- Mild Fish (Cod, Tilapia, Haddock): For these delicate varieties, lighter blends with lemon and parsley work best. As a result, the subtle flavors are complemented rather than overpowered.
- Rich Fish (Salmon, Tuna, Mackerel): For these types, bold spices like paprika, cayenne, or smoked salt are ideal, as they balance the rich, oily texture of the fish.
- Shellfish (Shrimp, Lobster, Crab): Pairing shellfish with garlic, paprika, and a hint of citrus creates a vibrant flavor profile that highlights their sweetness.
- Mixed Seafood (Paella or Stir-Fry): Versatile blends with a balance of herbs and spices bring cohesion to dishes with multiple types of seafood.
By understanding how seasoning interacts with different seafood types, you can ensure the flavors are always well-balanced and enjoyable.
Other Creative Uses
Seafood seasoning’s applications go beyond traditional recipes. For example:
- Breading: Mix the seasoning into breadcrumbs or flour to create a flavorful crust for fried or baked fish.
- Butter Sauce: Blend it with melted butter and drizzle over cooked seafood as a quick and easy finishing touch.
- Pasta: Toss cooked shrimp or scallops in seasoned butter and combine with pasta for a restaurant-quality dish.
In addition to these uses, seafood seasoning can even elevate vegetable-based dishes or side dishes, making it a versatile addition to any kitchen.
Health Benefits and Nutritional Value of Seafood Seasoning
Seafood seasoning not only elevates the flavor of dishes but also offers several nutritional benefits, depending on its ingredients. However, moderation is key to ensure a healthy balance, particularly if the blend contains salt or other high-sodium elements.
Low-Calorie Flavor Enhancements
One of the greatest advantages of seafood seasoning is its ability to add flavor without significantly increasing the calorie count of your meal. For example:
- Herbs and Spices: Ingredients like paprika, garlic powder, and thyme are low in calories but rich in flavor.
- Citrus Zest: Adding zest to the blend provides a burst of brightness with virtually no calories.
As a result, seafood seasoning is an excellent choice for those looking to enhance taste without compromising on calorie goals.
Benefits of Natural Ingredients
Seafood seasoning often includes herbs and spices that are packed with essential nutrients and health benefits:
- Paprika: Rich in antioxidants and vitamins A and E, which promote healthy skin and vision.
- Garlic Powder: Contains compounds like allicin that may boost the immune system and heart health.
- Parsley: A source of vitamin K, which supports bone health.
- Black Pepper: Contains piperine, known to aid digestion and enhance nutrient absorption.
By incorporating these natural ingredients, seafood seasoning can contribute to overall health while making meals more enjoyable.
Potential Sodium Concerns and Alternatives
- High Sodium Content
- Many commercial seafood seasonings use salt as a primary ingredient, which can contribute to excessive sodium intake. Over time, this may increase the risk of high blood pressure or other health issues.
- Low-Sodium or Salt-Free Options
- For a healthier alternative, opt for low-sodium blends or make your own seasoning at home. Replace salt with flavorful alternatives like:
- Lemon zest
- Dried herbs (e.g., oregano or basil)
- Spices like cumin or coriander
- For a healthier alternative, opt for low-sodium blends or make your own seasoning at home. Replace salt with flavorful alternatives like:
- Portion Control
- Use seafood seasoning sparingly, as a little can go a long way in enhancing flavor without overloading on salt.
Allergen Awareness
While seafood seasoning itself is not typically allergenic, some blends may contain trace amounts of allergens (e.g., shellfish-derived flavors or additives). Always read the label carefully if you have allergies.
Creative Variations of Seafood Seasoning
Seafood seasoning is incredibly versatile, allowing endless opportunities for customization to suit specific dishes and flavor preferences. By experimenting with different ingredients, you can create unique blends that highlight the natural taste of seafood while adding a personal touch.
Spicy Blends for Heat Lovers
For those who enjoy bold and fiery flavors, a spicy variation of seafood seasoning can enhance dishes like blackened fish or Cajun shrimp.
Ingredients to Add:
- Extra cayenne pepper or crushed red pepper flakes
- Chili powder for depth of spice
- Chipotle powder for a smoky kick
Best For: Grilled shrimp, spicy seafood pasta, or fish tacos.
Citrus-Infused Seasoning
Citrus elements add a bright, tangy flavor to seafood seasoning, complementing light and delicate dishes like white fish or scallops.
Ingredients to Add:
- Lemon or lime zest
- Dried orange peel
- A touch of citric acid powder for an extra zing
Best For: Baked cod, ceviche, or steamed mussels.
Herb-Forward Mixes for Delicate Seafood
For mild fish and seafood, an herbaceous seasoning blend can bring out their natural flavors without overpowering them.
Ingredients to Add:
- Fresh or dried dill
- Parsley for a light, grassy note
- Tarragon or chives for a subtle licorice flavor
Best For: Poached salmon, crab cakes, or creamy seafood soups.
Sweet and Smoky Combos
This variation balances sweetness and smokiness, ideal for rich or oily seafood like salmon and mackerel.
Ingredients to Add:
- Brown sugar or honey powder for sweetness
- Smoked paprika or liquid smoke for depth
- A pinch of allspice for warmth
Best For: Glazed salmon, grilled lobster, or roasted shrimp.
Mediterranean-Inspired Seasoning
This blend incorporates Mediterranean herbs and spices for a robust and aromatic profile.
Ingredients to Add:
- Oregano and thyme
- Basil for a sweet, peppery note
- A hint of fennel seeds for anise-like flavor
Best For: Grilled calamari, baked sea bass, or seafood-stuffed peppers.
Fusion Flavors
Combine elements from different cuisines to create a fusion-inspired seasoning:
- Asian Influence: Add ground ginger, sesame seeds, and a touch of soy powder.
- Indian Touch: Incorporate turmeric, cumin, and coriander for a curry-like blend.
- Caribbean Flair: Use allspice, nutmeg, and dried mango powder for a tropical twist.
Best For: Stir-fried shrimp, curried fish, or seafood skewers.
Salt-Free Options
For those watching their sodium intake, a salt-free seafood seasoning can still deliver plenty of flavor.
Ingredients to Add:
- Extra garlic powder, onion powder, and paprika for a savory base.
- Citrus zest and fresh herbs to enhance the taste naturally.
- Nutritional yeast for a cheesy, umami flavor.
Best For: Any seafood dish where salt-free alternatives are needed.
Storage and Shelf Life of Seafood Seasoning
Proper storage of seafood seasoning is essential to maintain its freshness, potency, and flavor over time. Whether you’ve made a homemade blend or purchased a store-bought option, following these tips will help preserve its quality.
Best Practices for Storing Homemade Blends
- Use Airtight Containers
- Store your seasoning in airtight containers, such as glass jars or plastic spice containers with tight-fitting lids. This prevents exposure to air, which can degrade the spices over time.
- Keep Away from Heat and Light
- Place the container in a cool, dry place, such as a pantry or spice cabinet. Avoid direct sunlight, as light can cause the spices to lose their vibrant colors and potency.
- Avoid Moisture
- Ensure the container is completely dry before storing your seasoning to prevent clumping or mold growth.
- Use a dry spoon when scooping seasoning to avoid introducing moisture.
Shelf Life of Seafood Seasoning
- Homemade Seafood Seasoning
- Typically lasts 6 months to 1 year when stored properly.
- For optimal freshness, consider making smaller batches to use within a few months.
- Store-Bought Seafood Seasoning
- Check the expiration date on the packaging.
- Once opened, aim to use the seasoning within 6–12 months for the best flavor.
Recognizing When Seasoning Has Gone Stale
- Loss of Aroma
- Fresh seasoning should have a strong, identifiable smell. If the aroma is weak or nonexistent, the blend has likely lost its potency.
- Faded Color
- Spices like paprika and herbs like parsley will fade over time. Dull colors indicate diminished quality.
- Texture Changes
- Clumping, dampness, or visible mold are signs that the seasoning has been exposed to moisture and should be discarded.
Pro Tips for Prolonging Freshness
- Label and Date: Clearly label your containers with the date the seasoning was made or opened to keep track of its age.
- Vacuum-Sealed Bags: For long-term storage, consider vacuum-sealing your seasoning to reduce air exposure.
- Small Containers: Divide large batches into smaller containers to minimize how often each one is opened.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Seafood Seasoning
Here is an improved version of the FAQ section with a higher density of transition words to ensure better flow and connectivity between sentences.
1. Can seafood seasoning be used on other proteins?
Yes, seafood seasoning can definitely be used on other proteins. For example, it pairs exceptionally well with chicken, pork, and even tofu. In particular, you can apply it as a rub for grilled chicken thighs, sprinkle it on roasted pork chops, or mix it with tofu before pan-frying to create a flavorful crust. Furthermore, its balanced blend of spices and herbs enhances a variety of dishes beyond seafood. Consequently, it has become a versatile staple in many kitchens.
2. How can I make seafood seasoning less salty?
If you find seafood seasoning too salty, there are multiple ways to adjust its saltiness. First of all, starting with a salt-free base allows you to control the amount of salt added later. Additionally, substituting regular salt with low-sodium salt or alternatives like potassium chloride is another effective method. Moreover, you can increase the proportions of herbs and spices in the blend to balance the flavors while keeping sodium levels in check. Therefore, these adjustments make it possible to enjoy flavorful seafood seasoning without worrying about excessive salt content.
3. Is seafood seasoning safe for shellfish allergies?
Seafood seasoning itself is generally safe for individuals with shellfish allergies since it does not typically contain shellfish. However, some store-bought blends may include seafood-derived additives or flavor enhancers. As a result, it is crucial to carefully examine the ingredient labels before purchasing. Alternatively, preparing your own blend at home ensures that it is free from any potential allergens. If you are ever in doubt, consulting the manufacturer or avoiding the product entirely is a wise choice.
4. What is the best seasoning for delicate fish like cod?
For delicate fish such as cod, it is essential to use a lighter, herb-forward seasoning. Specifically, ingredients like dill, parsley, lemon zest, and garlic powder complement cod’s mild flavor beautifully. On the other hand, stronger or smoky blends should be avoided, as they can easily overpower the fish’s natural taste. Consequently, opting for a subtle combination of herbs and spices ensures that the dish remains well-balanced and delicious.
5. How do I know if store-bought seasoning has additives?
To determine whether store-bought seasoning contains additives, it is important to read the ingredient list thoroughly. Common additives include anti-caking agents like silicon dioxide, artificial flavors, and monosodium glutamate (MSG). Furthermore, look for labels indicating that the product is “natural” or “free from preservatives” as a healthier alternative. Alternatively, making your own blend at home provides complete control over the ingredients, which eliminates any concerns about hidden additives.
6. Can I use seafood seasoning in vegetarian dishes?
Absolutely! Seafood seasoning is an excellent way to enhance vegetarian dishes. For instance, you can sprinkle it over roasted vegetables such as zucchini, bell peppers, and eggplant for added flavor. Additionally, it works well as a seasoning for grilled corn or avocado, giving them a smoky and tangy kick. Furthermore, incorporating it into soups or stews brings richness and depth to the dish. Consequently, seafood seasoning’s versatility makes it a valuable ingredient in both vegetarian and plant-based cooking.
Conclusion
In summary, seafood seasoning is a versatile and flavorful ingredient that enhances the natural taste of seafood while also being suitable for other proteins and vegetarian dishes. Moreover, its adaptability allows it to be used across various cuisines and cooking styles. Additionally, whether you opt for a store-bought blend or make your own, seafood seasoning provides endless opportunities to elevate your cooking. So, why not experiment with it in your next recipe? Undoubtedly, your dishes will be more flavorful and satisfying!